Large projecting eaves and wide verandahs are needed in composite climate as out-door living areas to reduce sky glare keep out the rain and provide shades. An architects aim would be to.
Passive solar systems basic rules-1.
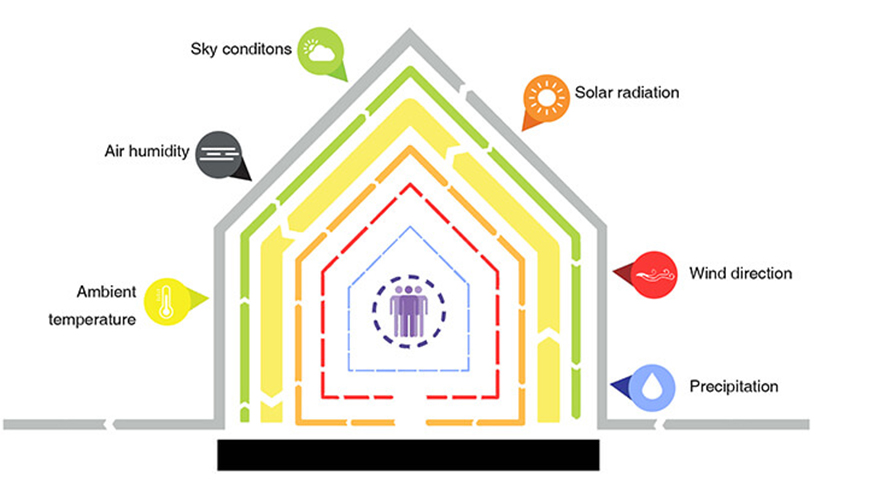
. And the sky conditions are againvariable which because it experiences all the 3 seasons. Design the devices to perform more than one function. Mahdavi and Kumar 1996.
Moreover there currently exists a lack of in-depth research on the influence of design strategies on the energy consumption of high-rise buildings in tropical climate Raji et al 2016. Various design strategies adopted in this building have been analyzed which can help in developing design considerations for Net Zero Energy Building NZEB in the composite climate. This communication presents design considerations and thermal performance of a hostel building using passive techniques for a composite climatic con.
The buildings south face should receive sunlight between the hours of 900 AM. Solar radiation outside air wet surfaces vegetation etc means in composite climate. Reduction in the humidity levels Continuous air circulation to reduce heat and relief from stickiness.
CLIMATIC CONSIDERATIONS PROJECTIONS. Compact form with low SV ratio is recommended. So composite climate receives3 distinct seasons summers monsoons and winters and the conditions vary in each ofthese seasons which is what the problematic causes.
Now the physiological objectivefor composite climate becomes very difficult. The air-conditioning and lighting consumption can be reduced by in- corporating climate-responsive features in the design. Climate responsive architecture takes into consideration seasonality the direction of the sun sun path and solar position natural shade provided by the surrounding topography environmental factors such as wind rainfall humidity and climate data temperature historical weather patterns etc to design comfortable and energy-efficient.
CLIMATE RESPONSIVE DESIGN STRATEGIES IN COMPOSITE CLIMATE In passive solar energy mechanical means are not employed to utilize solar energy. Design for climate means that a home is designed or modified to. Design and Use of Composite Indices in Assessments of Climate Change Vulnerability and Resilience 1 10 INTRODUCTION Composite index methodologies have evolved to meet a wide range of purposes and to inform particular decisions or decision-making processes.
Passive strategies provide thermal and visual comfort by using natural energy sources sinks. REQUIREMENTS IN A HOT AND HUMID CLIMATE Minimization of the high day temp. Considerations for buildings to become comfortable include realisation of an open barrier between the indoor and outdoor climate make use of solar and natural ventilation strategies and allowance for human intervention in climate control to satisfy subjective needs Fountain et al 1996.
This paper focuses on various bioclimatic design strategies Orientation of building plays a vital role in achieving energy for building design in a composite climate like Delhi. Recommendation for composite climate eg. The climate resilience design considerations for each of those linked sections as well as additional climate resilience resources by section are included in this document for easy reference.
CLIMATIC CONSIDERATIONS JALIS. Composite region Characteristics of the composite region are very hot and dry summer followed by a humid season with monsoon rains. The key of design take an advantage of local climate microclimate for human comfort.
An adaptive thermal comfort design is essential. Orient the buildings with longer axes in the east-west direction. Use minimal heating or cooling.
Jalis on the outer facade of the building helps in cooling shading and ventialtion. Incorporation of solar passive techniques in a building design helps to minimize load on conventional systems such as heating cooling ventilation light. And 300 PM during the.
East and west orientation should be protected by buffer spaces shaded walls etc. Hot-dry early summer warm-humid late summer monsoon period and cold-dry period in winter. The actual comfort conditions achieved will be contextual and depend on the building topology and building design specifications.
Avoidance of direct exposure of facades to solar radiations. There are certain design considerations for composite region buildings which should resist heat gain in summer and resist heat loss in winter. A rectangular form with a longer axis along the north-south is the preferred orientation.
The place experiences three definite seasons. The passive design strategies for composite climate and also presents the various methods of passive cooling techniques. Delhi and Gurgaon.
Examples include assessments of human development. The building should be elongated on an east-west axis. The scope of work for projects may include a copy of the completed RRVA for reference or the Design Consultant may request a copy.
A square plan with a courtyard would be very effective. This communication presents design considerations and thermal performance of a hostel building using passive techniques for a composite climatic condition of Delhi India.
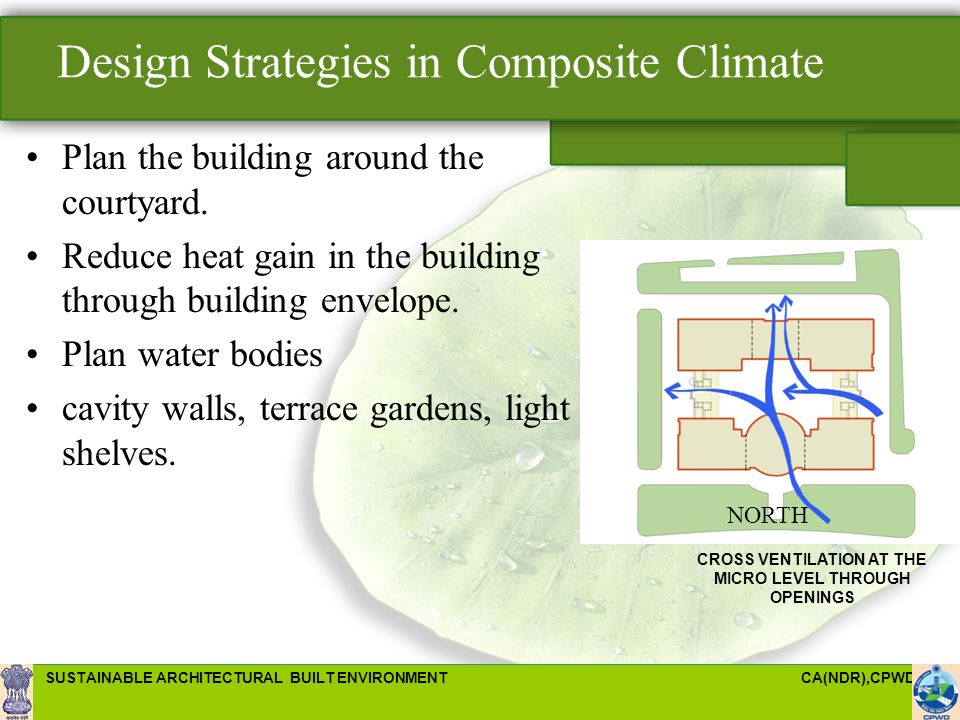
Sustainable Architectural Built Environment Ppt Video Online Download
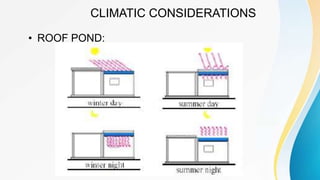
Architectural Features Of Composite Climate In India

Energy Efficiency For Composite Climate
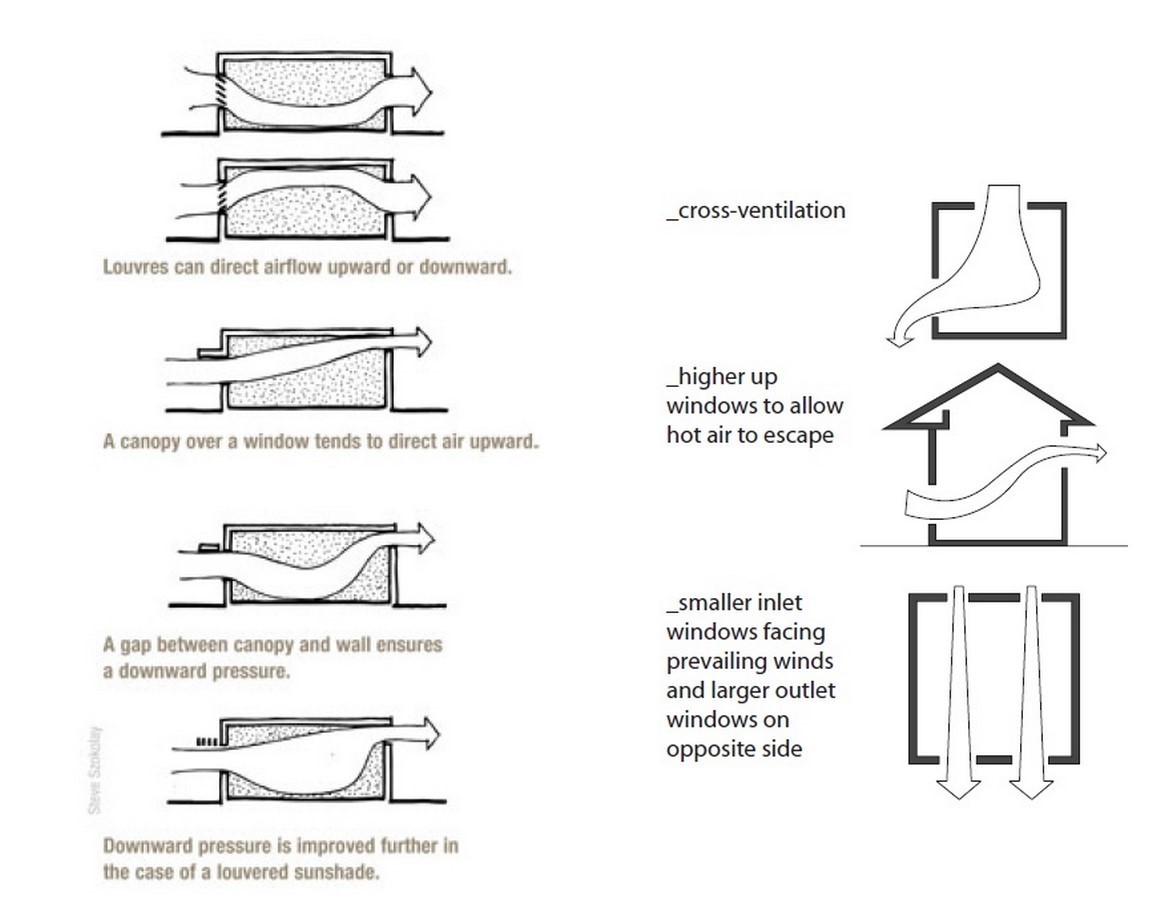
10 Things To Remember When Designing In Tropical Climate Rtf Rethinking The Future



0 comments
Post a Comment